Property and property relations have shaped the form of communities and the character of governance within them at every stage of human existence. Specific legal systems developed different notions of property and created rights and obligations based on them.
The right to property has always been recognized and maintained throughout history. The concept of private ownership was embraced by our forefathers. The concept of property, which was once limited to ownership and possession, has now expanded to include any object of economic value. Property has been divided into distinct categories and acknowledged. The right to acquire, own, and dispose of property is now a fundamental right guaranteed by the Indian Constitution, and its deprivation is banned unless by legal procedure.
The current classification of Intellectual Property
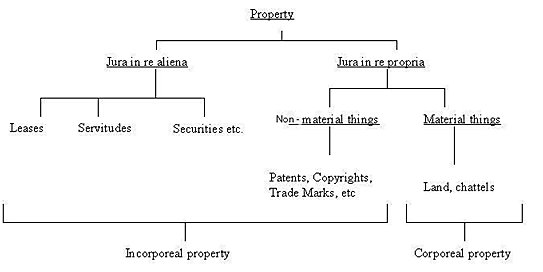
Every legal system creates laws that govern property possession and ownership. Property protection rules must be formulated in light of the current socio-economic and political climate.
Science and technological advancements have had an impact on the definition of property, adding a new dimension to the development of property protection legislation. Intellectual property arose from the emergence and development of changing laws in a socio, politico-economic technical environment.
Intellectual property law safeguards some of humanity’s finest achievements. In terms of intellectual property rights and their significance in innovation, the Philippines face a number of issues. Physical infrastructure deficiencies, significant intellectual capital but insufficient intellectual infrastructure, and a lack of public awareness are just a few of the roadblocks. The concerns of intellectual property development, valuation, protection, and exploitation have grown extremely essential all over the world.
Many of the features of intellectual property are similar to those of real and personal property. It’s a commodity that can be bought, sold, licensed, exchanged, or given out for free. Furthermore, the owner of intellectual property has the right to prevent the property from being used or sold without permission. Intellectual property differs from other types of property in that it is intangible, meaning it cannot be defined or identified by its own physical attributes.
To be protected, it must be expressed in some identifiable form. Intellectual Property (IP) rights are critical to maintaining a competitive edge in today’s dynamic and competitive corporate climate. Effective intellectual property acquisition, management, and protection can be the difference between commercial success and failure for a company.

